Rolling Door 101
Rolling Door 101
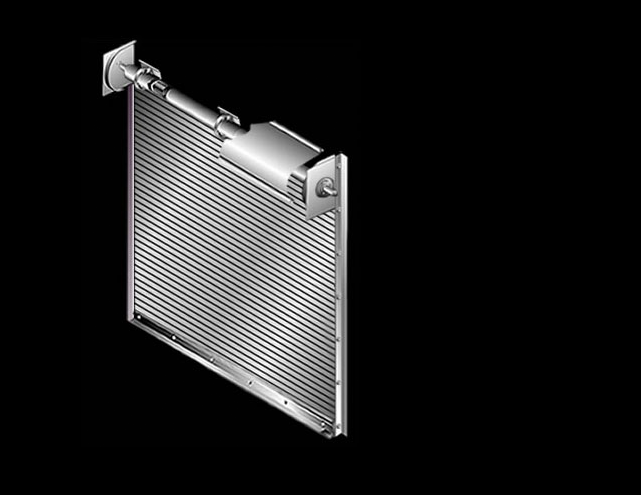
This diagram provides a general overview of the components of a rolling door. All materials referenced are standard, other options may apply.
Choose a part from the list to the left to see what it looks like an exploded view of it.

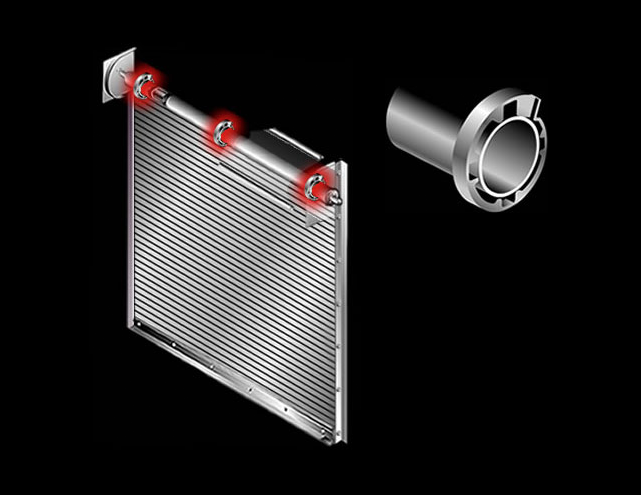
Adjustor Bracket: Steel plate that bolts to the guide assembly and supports the counter balance shaft and curtain
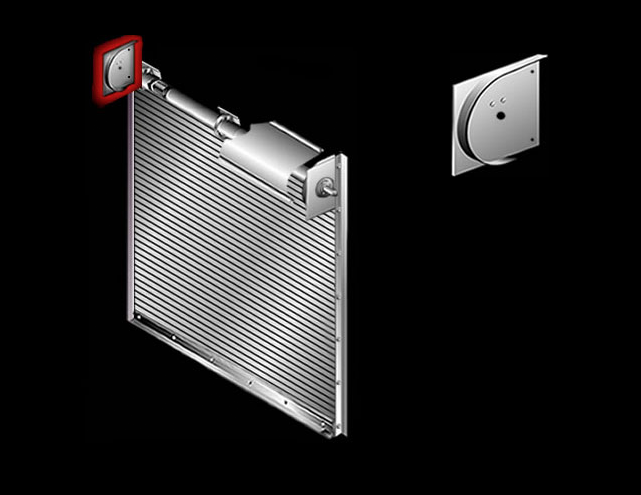

Hood: An optional aesthetic galvanized steel cover for the door coil area.
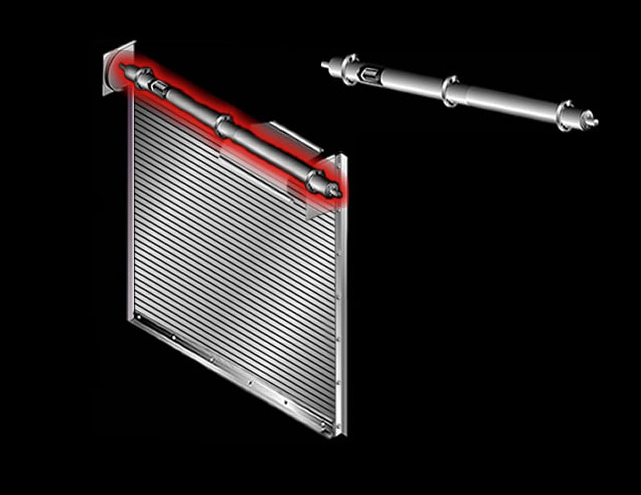
Counter-Balance Shaft: This steel assembly supports the curtain and contains counter-balance torsion springs for assisting operation
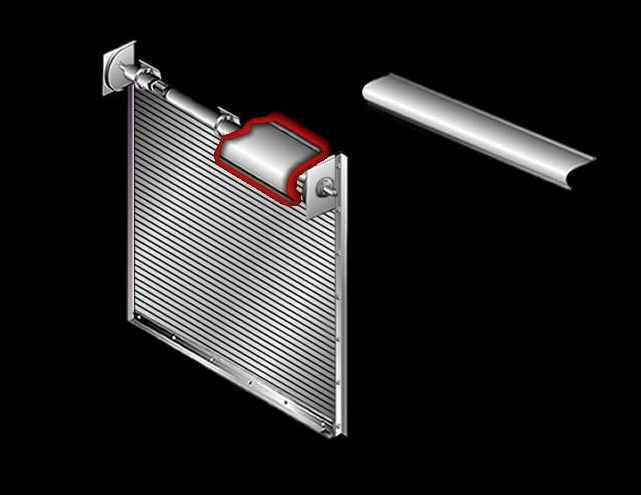
Curtain Endlocks: High strength nylon or cast iron parts attached to the ends of alternate slats to maintain slat alignment and serve as the loading surface with the guides.
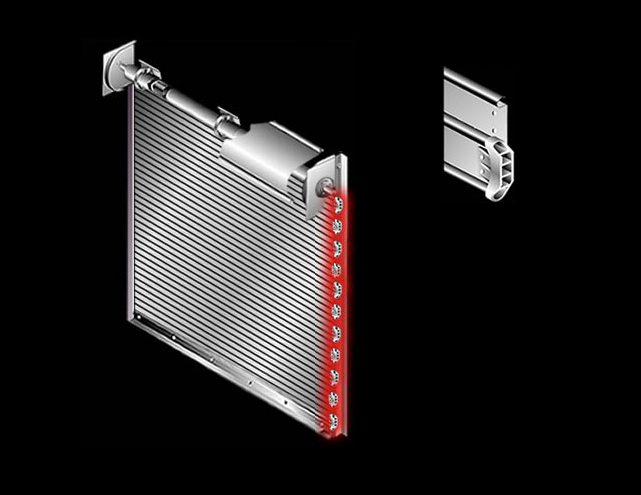

Curtain Fastening Section: For each shaft ring, an approximate 12" long section of heavy gauge curtain slat material is provided for attachment of the curtain to the shaft.
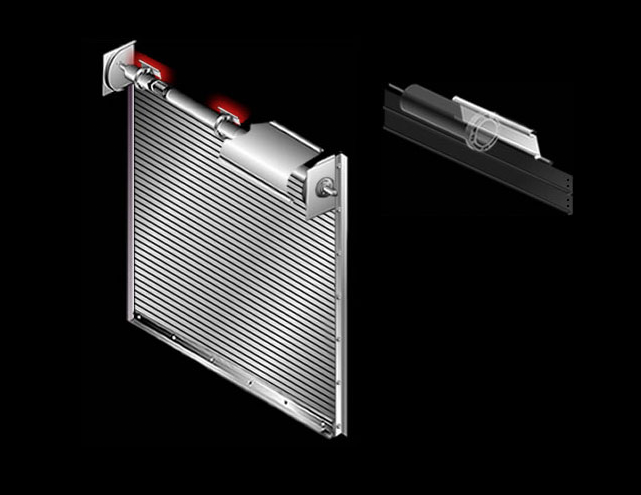

Door Bottom Bar: Extruded aluminum section at bottom of curtain. Can be equipped with weather-seal and lock mechanisms.
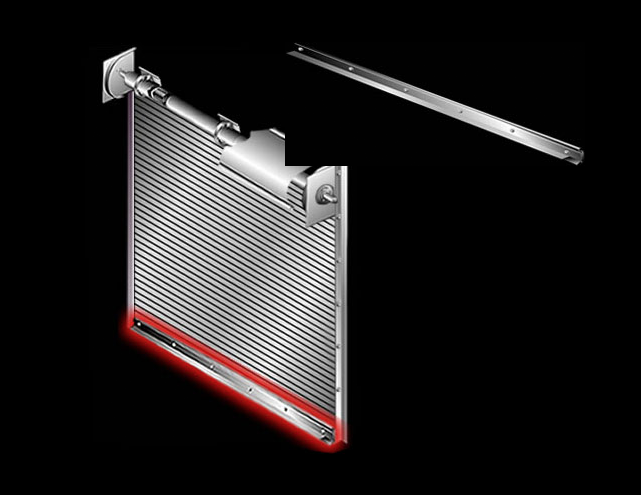

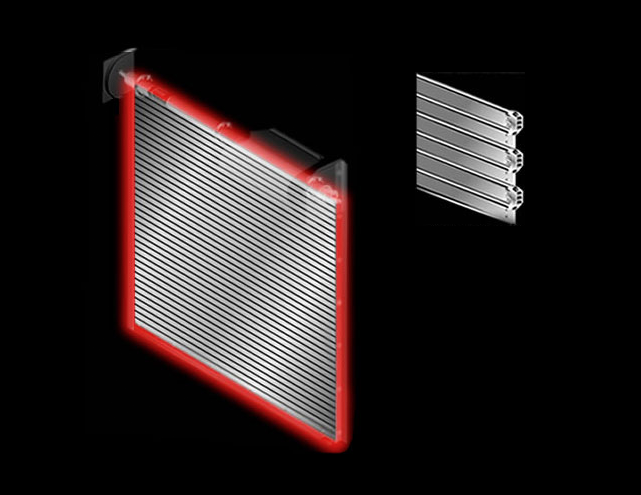
Curtain: Interlocking roll formed galvanized steel slats with endlocks attached to ends of alternate slats to maintain slat alignment We can design doors to meet your specific PSF wind load requirements.
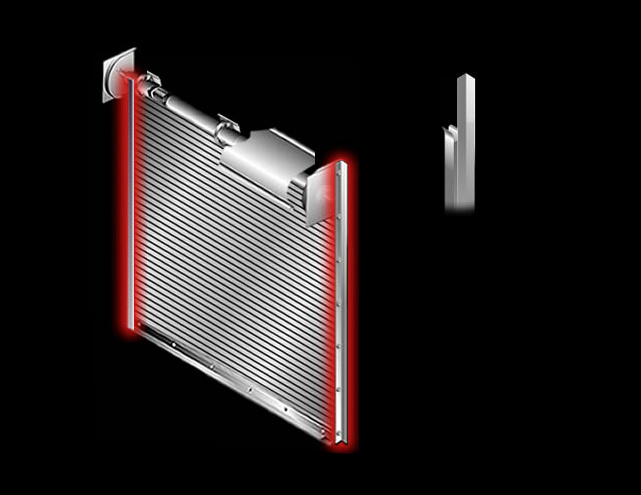
Guides: Assemblies of structural steel angles that support the entire door unit. Appropriate jamb support is required.
Guide Bellmouth: Located within the door coil area at the top of the inner and outer guide angles. The angles are coped and flared creating a "bellmouth" for easy entry of the curtain into the guides during normal operation.
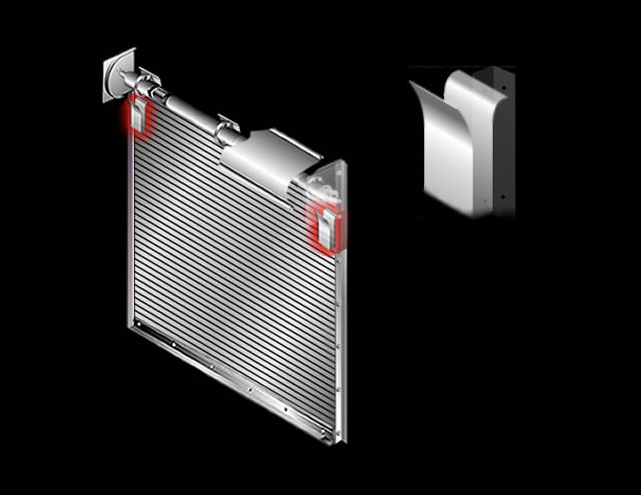

Operator Bracket: Steel plate that bolts to the guide assembly and supports the counter balance shaft and curtain.
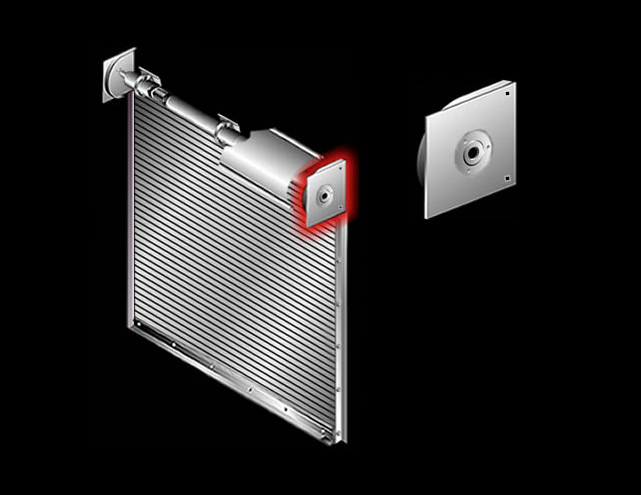

Shaft Ring: Cast iron or stamped steel rings attached to the shaft and curtain assembly that increase the initial coil diameter, which aids spring balance and coiling characteristics on doors with smaller diameter shafts.






